ISSN: 2206-7418
Nanotheranostics, the sister journal of Theranostics, is a multidisciplinary and fully open access journal. Nanotheranostics publishes innovative and original basic, translational and clinical research reflecting the fields of nanomedicine, nanoimaging, drug and gene delivery, nanoelectronic biosensors, and related areas.
Regular features include high quality research articles, reviews or mini-reviews, rapid communication of preliminary data on innovative research, editorials, and letters to the editor. Educational articles on basic sciences, fundamental aspects and controversy related to pre-clinical and clinical studies or ethical issues of nanomedicine are also welcome. Timely reviews that provide updates on current applications and issues in nanomedicine and translational aspects of nanotheranostics and other topics are particularly welcome and will be given high priority.
Nanotheranostics employs a rigorous peer-review system, but also strives for rapid review turnaround times and is based on the same streamlined submission platform as Theranostics.
Recent Papers:
Research Paper
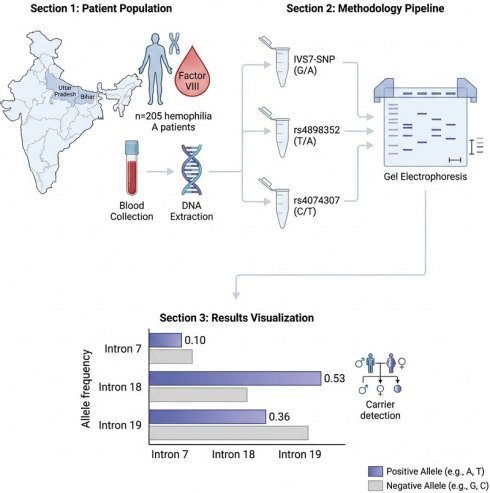
Molecular Characterization of Factor VIII Gene Variants in Hemophilia A: A Genotype-Haplotype Study from Eastern and Northern-Central India
Chanda Hemaliya, Arun Kumar Singh, Anju Bharti, Akhtar Ali, Lalit Prashant Meena
Nanotheranostics 2026; 10: 67-74. doi:10.7150/ntno.119985
Full text
PDF
Review
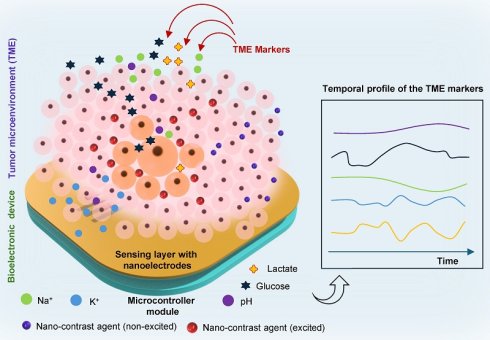
Bioelectronics for In Situ Monitoring of Tumor Microenvironment Markers
Kuldeep Mahato, Girijesh Kumar Patel
Nanotheranostics 2026; 10: 54-66. doi:10.7150/ntno.126464
Full text
PDF
PubMed
PMC
Research Paper
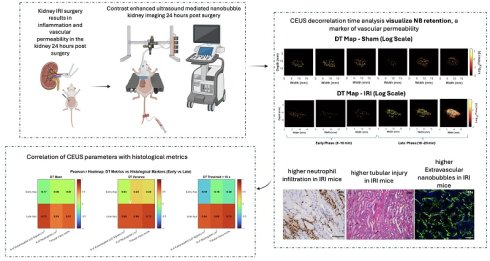
Quantification of Kidney Inflammation Using Nanobubble-mediated Contrast Enhanced Ultrasound
Niloufar Rostam Shirazi, Xiaolin He, Dana Dranka, Omar Falou, Eno Hysi, Agata A. Exner, Darren Yuen, Michael C. Kolios
Nanotheranostics 2026; 10: 38-53. doi:10.7150/ntno.126443
Full text
PDF
PubMed
PMC
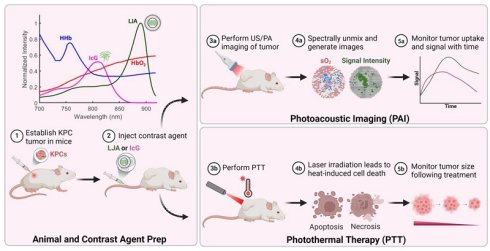
Research Paper
Liposomal J-Aggregates of Indocyanine Green as a Multifunctional Contrast Agent for Photoacoustic Imaging and Photothermal Therapy
Noah Stern, Binita Shrestha, Susan Burrell, James Tunnell, Tyrone Porter
Nanotheranostics 2026; 10: 24-37. doi:10.7150/ntno.123184
Full text
PDF
PubMed
PMC
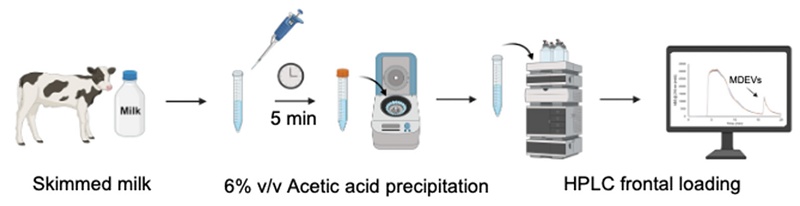
Research Paper
Rapid method for the high purity isolation of bovine milk-derived extracellular vesicles via polyester (PET) capillary-channeled polymer (C-CP) fiber columns
Carolina Mata, R. Kenneth Marcus
Nanotheranostics 2026; 10: 11-23. doi:10.7150/ntno.129284
Full text
PDF
PubMed
PMC
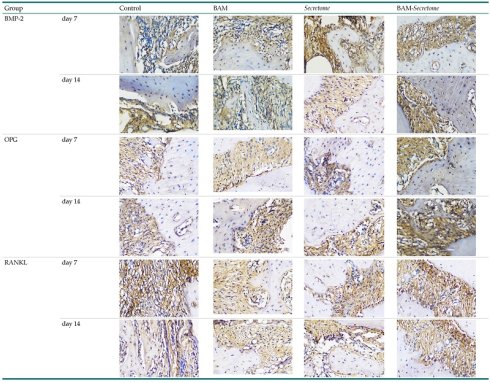
Research Paper
Expression of BMP-2, OPG, RANKL And Number of Osteoblasts After Application of Bovine Amniotic Membrane and Secretome Umbilical Cord in Wistar Rats
Ernie Maduratna Setiawatie, Lambang Bargowo, Shafira Kurnia Supandi, Vinanto Putero Negoro, Ferlina Diah Ayu Y. P. A., Elizabeth Luna K. A., Reinaldo Agusta, Nor Adinar Baharuddin
Nanotheranostics 2026; 10: 1-10. doi:10.7150/ntno.121118
Full text
PDF
PubMed
PMC
Editor-in-Chief:
Jonathan F. Lovell
SUNY Empire Innovation Professor
Department of Biomedical Engineering
University at Buffalo, State University of New York
Nanotheranostics has been selected by The Literature Selection Technical Review Committee (LSTRC) for inclusion in MEDLINE, the prestigious index of U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Full texts of articles in PubMed Central and Europe PMC. Abstracts in PubMed.
- Indexed in the Biological Abstracts and BIOSIS Previews of Web of Science.
- (For NIH-funded researchers) Save time by submitting your paper to us - this journal is in full compliance with NIH Public Access Requirement.
Impact Score: 8.25, h-Index: 38, SJR: 1.2, Overall Ranking: 3555, based on information from Resurchify, 2025.
Special Issue: Promising Contribution to Disease Diagnosis and Introduction of a Special Issue in Honour of Prof. Rohit Srivastava. Guest Editors: Prof. Amnon Bar-Shir, Dr. Rajendra Prasad, Prof. Y. Shrike Zhang, Dr. Mark Woollam, Dr. Berivan Cecen

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact