ISSN: 2206-7418
Nanotheranostics 2019; 3(1):66-88. doi:10.7150/ntno.30052 This issue Cite
Review
Biological Effects of Nanoparticles on Macrophage Polarization in the Tumor Microenvironment
1. Department of Neurosurgery, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA 90048
2. Biomedical Imaging Research Institute, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA 90048
3. Samuel Oschin Comprehensive Cancer Institute, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA 90048
4. Current Address: Department of Cell Biology and Biochemistry, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Lubbock, TX 79430, USA
Abstract
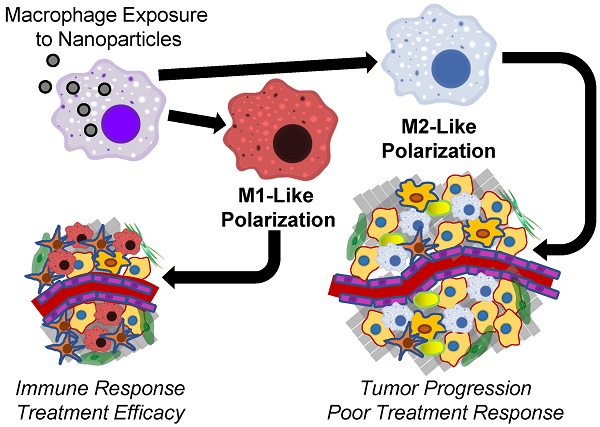
Biological interactions between tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), cancer cells and other cells within the tumor microenvironment contribute to tumorigenesis, tumor growth, metastasis and therapeutic resistance. TAMs can remodel the tumor microenvironment to reduce growth barriers such as the dense extracellular matrix and shift tumors towards an immunosuppressive microenvironment that protects cancer cells from targeted immune responses. Nanoparticles can interrupt these biological interactions within tumors by altering TAM phenotypes through a process called polarization. Macrophage polarization within tumors can shift TAMs from a growth-promoting phenotype towards a cancer cell-killing phenotype that predicts treatment efficacy. Because many types of nanoparticles have been shown to preferentially accumulate within macrophages following systemic administration, there is considerable interest in identifying nanoparticle effects on TAM polarization, evaluating nanoparticle-induced TAM polarization effects on cancer treatment using drug-loaded nanoparticles and identifying beneficial types of nanoparticles for effective cancer treatment. In this review, the macrophage polarization effects of nanoparticles will be described based on their primary chemical composition. Because of their strong macrophage-polarizing and antitumor effects compared to other types of nanoparticles, the effects of iron oxide nanoparticles on macrophages will be discussed in detail. By comparing the macrophage polarization effects of various nanoparticle treatments reported in the literature, this review aims to both elucidate nanoparticle material effects on macrophage polarization and to provide insight into engineering nanoparticles with more beneficial immunological responses for cancer treatment.
Keywords: Nanoparticles, Macrophage polarization, Tumor microenvironment, Cancer, Iron oxide

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact