ISSN: 2206-7418
Nanotheranostics 2023; 7(1):41-60. doi:10.7150/ntno.76720 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Ultra-small NIR-Responsive Nanotheranostic Agent for Targeted Photothermal Ablation Induced Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPs) from Post-PTT of Tumor Cells Activate Immunogenic Cell Death
1. Bio-Nano Therapeutics Research Laboratory, Cancer Research Program (CRP), Department of Zoology, Bharathiar University, Coimbatore-641 046, TN, India.
2. Department of Biochemistry, Prof. Dhanapalan College of Science and Management, Chennai, India.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
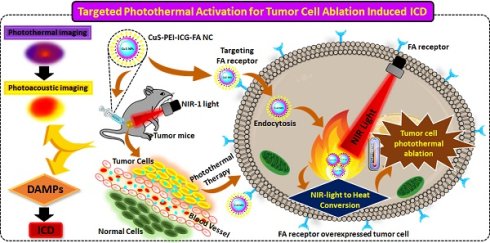
Theranostic nanoparticles (TNPs) is an efficient avenue that culminates both diagnosis and therapy into cancer treatment. Herein, we have formulated a theranostic nanocomposite (NC) with CuS being the ultra-small core component. To ensure stability to the NC, PEI was added which is a vital anchoring group polymer, especially on sulfide surfaces, and adds quality by being a better stabilizer and reducing agent. Additionally, to add stability, specificity, and added photothermal efficiency to the fabricated NC. In addition, encapsulation of indocyanine green (ICG), an efficient NIR absorber, and Folic acid (FA) were conjugated systematically, characterized, and analyzed for photo-stability. The photothermal conversion efficiency of the novel NC (CuS-PEI-ICG-FA) was analyzed at 808 nm, where the NC efficiently converted light energy to heat energy. The NC was also tested for hemocompatibility to clarify and also determined biocompatibility. Surprisingly, damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) from post-PTT of tumor cells activate immunogenic cell death (ICD) for tumor-specific immune responses. The deserving photothermal performance and photo-stability makes the NC an ideal platform for photoacoustic imaging (PAI). A superior contrast was observed for PAI in a concentration-dependent manner enhancing the level of penetration into tissues, thereby better imaging. On account of this study, the newly formulated NC could be utilized as a “nanotheranostic” designed for therapeutic and image diagnostic agent of cancer biomedical applications.
Keywords: Nanotheranostic, Photothermal therapy, Photoacoustic imaging, Immunogenic cell death, Cancer

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact