ISSN: 2206-7418
Nanotheranostics 2023; 7(2):210-215. doi:10.7150/ntno.81485 This issue Cite
Editorial
Personalized biosensors for point-of-care diagnostics: from bench to bedside applications
Laboratory of Bio-physio Sensors & Nanobioengineering, School of Biochemical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology (BHU) Varanasi, Varanasi 221005, Uttar Pradesh, India
Abstract
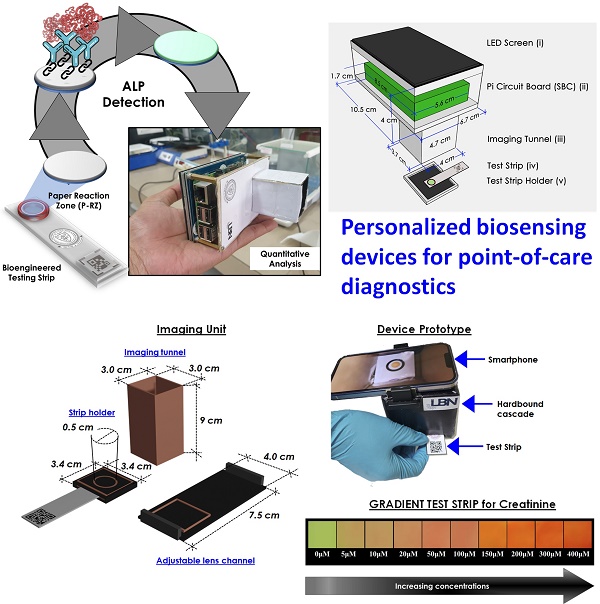
The most significant feature of translational point-of-care technology “Personalized biosensors” is that it can be done quickly and by clinical staff who are not trained in clinical laboratory sciences. Rapid test results can quickly give a doctor or other medical worker answers that can help them decide what to do or how to treat a patient. This is helpful almost everywhere, from the emergency room to a patient getting care at home. When a doctor meets a patient for the first time, during a flare-up of a known problem or when a new symptom shows up in a patient who is already being treated, having faster access to test results gives the doctor answers when they are with the patient or are about to see the patient which indicate the importance of point-of-care technologies and their future scope.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact