ISSN: 2206-7418Nanotheranostics
Nanotheranostics 2024; 8(4):442-457. doi:10.7150/ntno.91871 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Dual Functional Magnetic Nanoparticles Conjugated with Carbon Quantum Dots for Hyperthermia and Photodynamic Therapy for Cancer
1. National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, Kolkata, West Bengal, 700054, India
2. National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, 382355, India.
3. Department of Immunology and Microbiology, School of Medicine, University of Texas, Rio Grande Valley, McAllen, TX 78504, USA.
# These authors equally contributed to this work.
Abstract
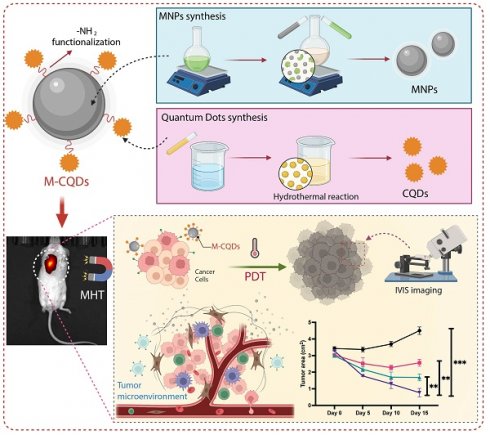
The global incidence of cancer continues to rise, posing a significant public health concern. Although numerous cancer therapies exist, each has limitations and complications. The present study explores alternative cancer treatment approaches, combining hyperthermia and photodynamic therapy (PDT). Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) and amine-functionalized carbon quantum dots (A-CQDs) were synthesized separately and then covalently conjugated to form a single nanosystem for combinational therapy (M-CQDs). The successful conjugation was confirmed using zeta potential, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), and UV-visible spectroscopy. Morphological examination in transmission electron microscopy (TEM) further verified the conjugation of CQDs with MNPs. Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) revealed that M-CQDs contain approximately 12 weight percentages of carbon. Hyperthermia studies showed that both MNP and M-CQDs maintain a constant therapeutic temperature at lower frequencies (260.84 kHz) with high specific absorption rates (SAR) of 118.11 and 95.04 W/g, respectively. In vitro studies demonstrated that MNPs, A-CQDs, and M-CQDs are non-toxic, and combinational therapy (PDT + hyperthermia) resulted in significantly lower cell viability (~4%) compared to individual therapies. Similar results were obtained with Hoechst and propidium iodide (PI) staining assays. Hence, the combination therapy of PDT and hyperthermia shows promise as a potential alternative to conventional therapies, and it could be further explored in combination with existing conventional treatments.
Keywords: cancer, nanoparticles, magnetic nanoparticles, quantum dots, hyperthermia, photodynamic therapy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact