ISSN: 2206-7418
Nanotheranostics 2019; 3(1):41-53. doi:10.7150/ntno.28450 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Intelligent Photosensitive Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Cell-Derived Microvesicles for Photothermal Therapy of Prostate Cancer
1. Department of Urology, Shanghai East Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai, 200120, China.
2. Shanghai East Hospital; The Institute for Biomedical Engineering & Nano Science, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai, 200120, China.
3. The State Key Laboratory of Refractories and Metallurgy, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430081, China.
4. Institute of Acoustics, Tongji University, Siping Road 1239, Shanghai 200092, China.
5. Key Laboratory of Stem Cell Biology, Institute of Health Sciences, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences/Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China.
Abstract
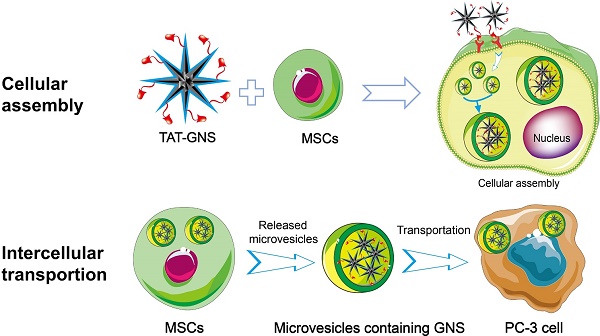
Targeted delivery of nanomedicines into the tumor site and improving the intratumoral distribution remain challenging in cancer treatment. Here, we report an effective transportation system utilizing both of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and their secreted microvesicles containing assembled gold nanostars (GNS) for targeted photothermal therapy of prostate cancer. The stem cells act as a cell carrier to actively load and assemble GNS into the lysosomes. Accumulation of GNS in the lysosomes facilitates the close interaction of nanoparticles, which could result in a 20 nm red-shift of surface plasmon resonance of GNS with a broad absorption in the near infrared region. Moreover, the MSCs can behave like an engineering factory to pack and release the GNS clusters into microvesicles. The secretion of GNS can be stimulated via light irradiation, providing an external trigger-assisted approach to encapsulate nanoparticles into cell derived microvesicles. In vivo studies demonstrate that GNS-loaded MSCs have an extensive intratumoral distribution, as monitored via photoacoustic imaging, and efficient antitumor effect under light exposure in a prostate-cancer subcutaneous model by intratumoral and intravenous injection. Our work presents a light-responsive transportation approach for GNS in combination of MSCs and their extracellular microvesicles and holds the promise as an effective strategy for targeted cancer therapy including prostate cancer.
Keywords: mesenchymal stem cells, microvesicles, gold nanostars, targeted transportation, photothermal therapy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact